Face Recognition: Everything You Need to Know
By mapping facial traits from a picture or video and then comparing the data with a database of recognized faces, facial recognition technology enables the identification of a human face using biometrics.
Moreover, face recognition is widely used—from the cameras at your favorite venue to the phone in your pocket—and the market for it is only expanding. By 2030, it is predicted to reach $16.74 billion, a rise of more than 125% from its 2020 value.
Cutting these things out, let us get started with the subject and understand its nuances in detail

Face Recognition: What Is It?
Facial recognition is a biometric technique that identifies a person based on the distinctive features of their face. It works by examining the features and patterns on faces to produce a distinct template known as facial data, which is used to identify individuals.
This technology can also identify faces in video broadcasts, even when the subject’s face is partly hidden. Although face recognition may identify a person only by looking at them it is usually used in combination with additional biometrics and authentication methods.
Facial recognition pros
We’re still learning about the benefits and drawbacks of a tool for common people. Here are a few of the main benefits:
- Travel Safer: To detect offenders or possible threats, airports utilize this technology.
- Criminal Identification: Suspects might be recognized by facial recognition in images or videos.
- Locate Those Who are Missing: Facial recognition technology has been used to identify individuals who are missing.
- Maintain the Security of Your Phone: Nowadays, a lot of phones employ this feature to unlock or confirm your identity before you buy.
Cons of Facial Recognition
It’s paramount to understand the limitations of AI face recognition. For instance, in 2022, Randal Reid was wrongly recognized by the software, leading to his arrest and one week of imprisonment. The crime was committed in Louisiana, a state he had never visited.
The following are a few of the main drawbacks of face recognition:
- Identity Error: If the technology is all that is used, it can be possible to mistakenly identify criminal suspects.
- Errors About Senior Citizens: As individuals age, facial recognition accuracy decreases.
- Bias Based on Race and Gender: Research has shown that women and persons of color are harder to recognize using this software.
- It is Foolable: Facial recognition can be rendered less accurate by wearing a mask, sunglasses, or even some types of cosmetics. .
- It Presents Threats to Security: It is possible to gather and keep face data, often without your consent. That data might be accessed by hackers and taken.
- Possible Ownership Problems Exist: When you consented to social media privacy regulations, you could have given away ownership rights over photos of your face.
How Facial Recognition Works
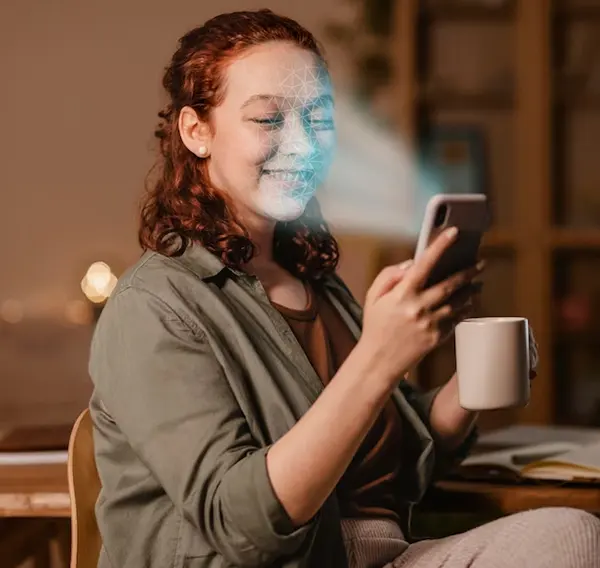

Applications for face identification combine machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and statistical analysis. This also includes image processing to identify faces in bigger pictures and separate them from non-facial items like buildings, landscapes, and other human body parts. The evaluated material is preprocessed to enhance quality and eliminate pictures that might impede detection before face detection starts.
Usually, face identification algorithms begin by looking for human eyes, which are among the simplest traits to identify. Next, they look for features on the face such as the lips, nose, irises, eyebrows, and nostrils. The algorithm does extra tests to verify that it has identified a face after determining that it has located a facial area.

The algorithms are trained on massive data sets including hundreds of thousands of positive and negative photos in order to guarantee accuracy. The algorithms’ capacity to identify faces in a picture and their location is enhanced by the training.
Could Face Recognition Take the Role of Passwords?
Yes, since OTPs (one-time passwords) and passwords today still signify something we may forget, face recognition technologies are much more secure than those methods. Not only that, but others possibly easily learn.
The European Union’s Payment Services Directive (PSD2) outlines three security tiers or methods for identity verification:
- Possession (something you have): Physical access cards, GPS locations, and even mobile phones fall within this category.
- Knowledge (something you know): passwords and private data, including our address, are located here.
- Inheritance (something you are): this category only includes things like our voice or looks that make us special and that others cannot have in our place.
Biometric identification systems are the safest method of identity verification because they let individuals be recognized for who they really are—their necessary qualities.
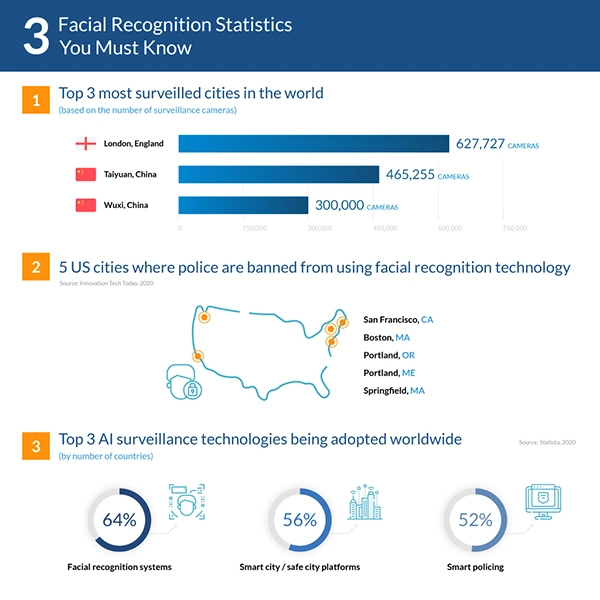
Conclusion
As facial recognition software is still in its relative infancy, the laws governing this area are evolving (and sometimes non-existent). Despite the risks, the systems are convenient and hard to duplicate. These systems will continue to develop in the future — the challenge will be to maximize their benefits when minimizing their risks.