How Computer Vision Transforms Pixels Into Insights
The introduction of functional computer vision heralds a new era of innovation across all industries.
It has triggered transformative changes in the way businesses operate and innovate sustaining them for a long time.
It enables businesses to automate processes, improve their efficiency, and enhance consumers’ experiences.
This groundbreaking technology also empowers organizations to extract meaningful insights from visual data.
Utilizing modern tech impactfully opens up unprecedented possibilities for creativity and problem-solving.
Computer vision will become a catalyst for innovation, enabling novel solutions to complex challenges and sparking entirely new ideas.
This article looks into the birth and transformative powers of computer vision from pixels to insights for limitless possibilities.
What Is Computer Vision?

The goal of computer vision is to replicate what the human visual system can do. For humans, it is very easy to look at photographs and interpret what they see.
They can express this interpretation in words, numbers, or other images. However, conventional robotics struggle to derive meaning from even the simplest of pictures.
CNNs

The first systems capable of true computer vision were CNNs. They dominated the field for over a decade since AlexNet debuted in 2012.
CNNs are typically trained on large datasets of images, after which they can be used for various duties, such as object recognition.
A major drawback of CNNs is the costly and time-consuming requirement for training. They also need a large dataset of pictures to enable this training.
CNNS are also rather inflexible because they are only trained in a particular way. They then cannot be repurposed without starting over with entirely new training.
While CNNs have been widely applied and have empowered innovation, they have made very few advances since their launch.
Transformers
Computer vision transformers are based on the models used for natural language processing, popularly called chatbots.
Transformers handle pictures by turning them into sequences of image patches. Then they embed each image patch into a feature map model.
Transformers can dynamically focus their attention on specific features of images, depending on the context.
They can also use a global view and observe the entire image rather than features or details within the image.
FUN FACT
Early experiments in computer vision took place in the 1950s, using some of the first neural networks to detect the edges of an object and to sort simple objects into categories like circles and squares.
CNNs Versus Transformers
This ability to refocus their attention is one of the primary characteristics distinguishing transformers from CNNs.
CNNs are unable to change their focus depending on the context and must follow their training.
If a user decides they want to, say, switch from looking for birds in pictures to looking for flowers, a transformer can readily do so.
A CNN would have to be completely restrained before it could handle the new duty. CNNs are also limited in that they can only look at features and details.
They cannot take a global view of the entire image. In general, advanced computation powered by transformers are more agile and intuitive.
However, for some specialized duties, a well-trained CNN can outperform a transformer.
Advantages Of Computer Vision
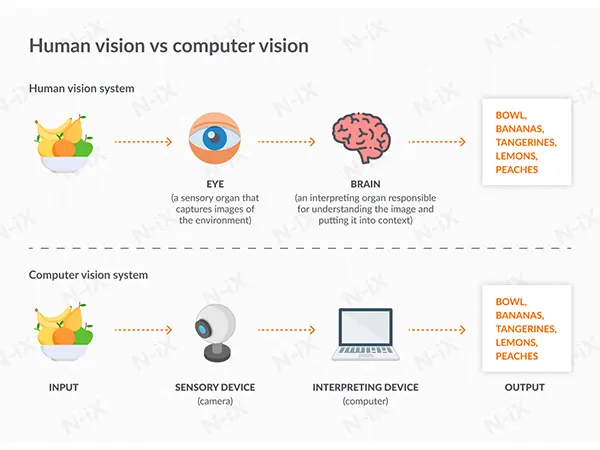
A typical computer vision system has cameras to gather images, a machine learning model to analyze the pictures, and conditional logic to automate an application-specific output.
For example, an automated visual system could monitor employees (with cameras) working in an area that requires the use of specific personal protection equipment (PPE).
If an employee experiences a rip or tear in their PPE, or someone tries to enter the area without proper PPE, the system would spot the infraction and sound an alarm.
Some well-known current uses of computer vision include:
- Quality control
- Monitoring
- Inspection
- Skill training
Tireless
The advantages of computer vision over human workers for many duties are generally obvious.
A computerized visual system can precisely analyze huge numbers of pictures around the clock without getting bored, distracted, or tired.
Subtle Changes
Computer visual systems can also detect features in images that humans are unable to detect.
For example, some systems can detect minute alterations in pictures of foundations. It means that the foundation is suffering from structural damage.
These alterations are so subtle that humans cannot see them which is an advantage of advanced robotics.
Other systems can detect flying insects in pictures and count and categorize them by species, a tedious chore few human observers can perform.
Other examples are systems that can notice signs of crop malnutrition or infestation that are so subtle human observers cannot detect them.
A computerized system can spot cleverly camouflaged objects humans are trying to hide; and so forth.
Business Transformation Powered By Computer Vision
The applications of computer vision in business are endless. Many have not even been imagined yet.
It has the potential to streamline and automate processes and perform processes managers have always dreamed of performing but never could.
It can also collect vital data that businesses can use to inform, streamline, and leverage their business strategies.
Computer Vision Examples
A business could use a computer visual system to monitor the production of their product and apply it to inspect the finished product.
It is a significant part of the quality-control process and collects data on consumer behavior to tailor their marketing strategy to specific populations.
They could also use it to improve the efficiency of their production process and secure their factory.
This ensures the quality of their raw materials and monitors their overseas business partners’ compliance with fair trade practices.
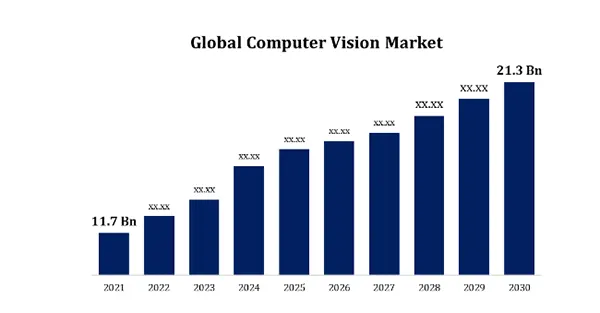
The graph below shows the global computer vision market size since 2021 which is forecasted to grow exponentially till 2030.
Future of Computer Vision
The advancement in computation visual systems in the future will expand beyond the automation of routine work.
It will transform the simple work of the collection of data into a valuable tool for innovation.
Businesses can use it to provide the insights necessary to spark the creative process, streamline their operations, and leverage their advantages.
Companies will need to partner with AI consulting firms to fully exploit this new technology.
Transforming Pixels Into Insights
The ability of advanced computerization to deeply analyze images allows humans to appreciate and understand details in a new way.
For example, computer vision analysis of athletes performing movements basic for their sport.
It has sparked the development of footwear, apparel, protective equipment, and training procedures that enhance their performance.
Transforming And Streamlining The Bottom Line
With tech transforming our lifestyle, computer visual analysis of how consumers navigate and interact in retail settings has provided new insights.
It improves customer experience, promotes purchasing, and streamlines the entire process, increasing profits and the happiness of users.
Conclusion
The integration of computer vision into business represents a revolutionary paradigm shift. It has created cutting-edge technology and reshaped traditional operational landscapes.
It enables businesses to extract valuable insights from visual data, transforming the way they operate and make decisions.
From automating routine work to enhancing customer experiences, organizations can harness the power of advanced tech.
They can utilize its systems to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
The integration of computer vision into businesses will trigger a wave of innovation, paving the way for unprecedented advancements.
As businesses embrace this transformative tech, they will achieve higher levels of productivity based on data-driven decision-making.