Understanding IoT Development: A Beginner’s Guide
Today’s interconnected world is filled with smart devices like phones, watches, and cars talking to each other. The magic behind this communication is IoT or the Internet of Things. It refers to the integration of data analytics and internet connectivity in the various objects that alter the way we work and live.
In other words, IoT is the connectivity of everyday objects with the internet and gets recognized by other devices to contribute information to the database. It’s a dynamic field, changing how businesses operate and people live. Companies like Vakoms specialize in IoT solutions, helping clients leverage this technology’s power.
Understanding IoT-development can seem complex, with devices, sensors, and apps interacting. In this article, we will guide you regarding everything related to IoT development and simplify the process for you to explore the fascinating IoT development world.
What is IoT Development?
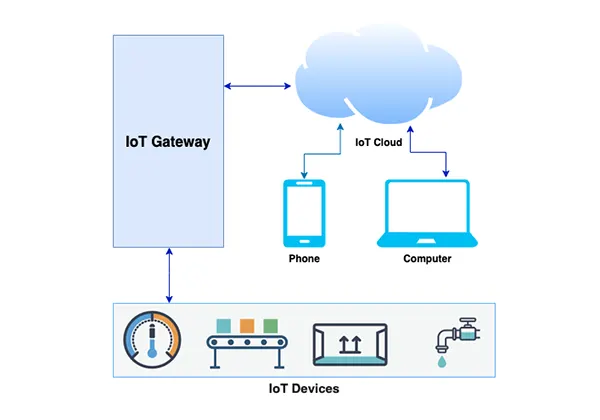
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an exciting field that brings together many technologies. It involves creating networks of devices that can communicate with each other and share data. These devices have sensors that can collect information about their surroundings, like temperature, humidity, or motion.
They also have small computers that can process this data and send it to other devices or the cloud. The key to developing the Internet of Things is connecting all these gadgets together so they can work as one big system.
IoT systems are used in many areas. In agriculture, farmers use sensors to monitor the soil, weather, and health of their crops. This helps them make better decisions about when to water, fertilize, or harvest. In smart buildings, IoT systems control things like heating, lighting, and security.
Phases of IoT Development
Crafting robust Internet of Things solutions demands a methodical progression through multiple phases:
Conceptualizing the Vision:
This initial step involves pinpointing the core challenge, specifying the devices to interconnect, and mapping out how the unified system will operate. The main focus of IoT is on the market needs to increase the connectivity between the network of devices.
These objects integrated with Internet-related protocols such as IPv4 and functioned accordingly. Such devices send information that is translated into a common, unified format, through which it can be analyzed on multiple aspects to get useful data.
Architecting the Framework:
Here, the intricate blueprint of the system’s architecture takes shape, coupled with the judicious selection of an apt IoT platform. It means a tangle of various elements such as sensors, cloud services, actuators, protocols, and layers that form a networking system.
It is generally categorized into parts, allowing administrators to evaluate, monitor, and maintain system integrity. Not only that, but it is a four-step procedure involving the flow of data from devices to sensors via the network and then through the cloud for processing, analysis, and storage.
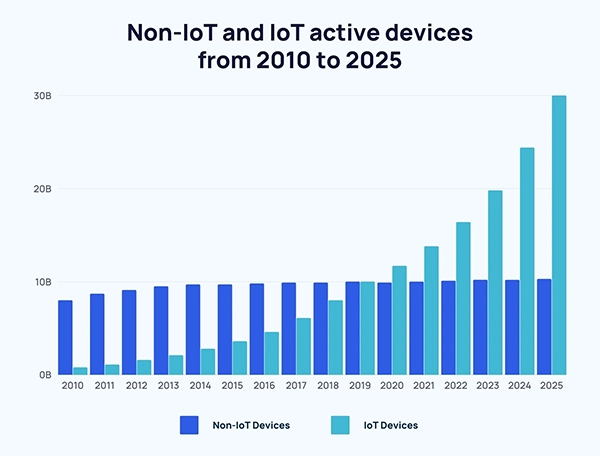
The following statistics represent the non-IoT and IoT active devices from 2010 to 2025.
Development Phase:
This is a vital phase of IoT development as it involves connectivity between hardware and software layers, enabling seamless internet connectivity for the devices.
At the prototyping level, the objective of the User interface is to prove the product’s value to users by building a front-end system displaying the data generated by the IoT system in real-time.
In addition, the role of hardware components is to procure and build the configuration of IoT products, to minimize the cost of prototypes and efforts can be minimized.
Rigorous Testing and Integration:
At this stage, the IoT system undergoes testing, which helps in identifying and making necessary adjustments to ensure the smooth functioning of different devices that are connected. Plus, rigorous testing makes sure that the smooth functioning of system performance and optimization of IoT devices
Deployment and Ongoing Maintenance:
The final phase entails rolling out the system into its operational environment, accompanied by continuous monitoring and upkeep to ensure its smooth functioning. It involves expanding from consumer-based applications like smart home devices and wearables to system applications in the areas of public safety, autonomous vehicles, and the healthcare field.
Each phase plays an indispensable role in realizing the successful implementation of an IoT solution.
Key Components of IoT Development
IoT development relies on several vital elements:
Hardware:
Physical components like sensors, actuators, and microcontrollers for IoT’s core. They gather data and transfer it to software for processing. These devices create the foundation.
Software:
Software includes firmware, middleware, and applications. Firmware controls hardware operations. Middleware connects devices and cloud platforms. Applications analyze data insights for informed decisions.
Connectivity:
Establishing secure, dependable links between IoT devices and cloud platforms enables seamless data flow. Technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks offer connectivity suited to specific use cases.
Do You Know?
The Concept of IoT Goes Back to the Mid-1800s
IoT Protocols and Connectivity
Communication protocols create a necessary aspect when designing IoT systems. Protocols determine how devices exchange data reliably and efficiently. Common protocols include:
- MQTT: A lightweight protocol suited for small sensors and mobile devices. It allows for efficient messaging over constrained networks.
- CoAP: Optimized for resource-constrained environments, CoAP operates over UDP, making it ideal for low-power networks.
- HTTPS: Provides secure data transmission over the internet, ensuring privacy and integrity.
IoT devices can connect via various technologies, each offering different range of capabilities:
- Wi-Fi: Commonly used in smart home automation solutions.
- Bluetooth: Perfect for short-range device-to-device communication.
- NFC: Enables simple, tap-based connectivity for quick interactions.
- Cellular Networks: Offer broad coverage through GSM, LTE, and the emerging 5G networks.
- LPWAN: Designed for long-range, low-power scenarios, allowing devices to run on batteries for years.
Selecting the appropriate protocol and connectivity option is vital. It ensures seamless device interaction and efficient data exchange within an IoT ecosystem.
Challenges in IoT Development
Constructing IoT applications poses several hurdles for developers.
Security:
Ensuring the safety of IoT ecosystems is necessary as connected devices multiply. Weaknesses in hardware, firmware, and communication protocols could expose devices to cyber threats. This compromises data integrity and user privacy.
Interoperability:
IoT solutions frequently involve diverse devices from various manufacturers, leading to compatibility challenges. Standardization efforts like MQTT and CoAP protocols aim to facilitate seamless integration across different ecosystems.
Scalability:
As IoT deployments expand to accommodate vast numbers of devices, scalability becomes paramount. Designing architectures capable of handling large data volumes and accommodating future growth without performance degradation is essential for long-term success.
Best Practices for IoT Development
The Internet of Things (IoT) development follows specific guidelines to ensure effective security and security.
Security from the Start:
Implementing security measures at every stage is vital. From device setup to data transmission, techniques like encryption, authentication, and secure boot protect against cyber threats. This approach mitigates potential risks.
Data Management Strategies:
Efficient data management extracts valuable insights from IoT deployments. By leveraging data analytics tools and techniques, organizations can derive meaningful information from raw sensor data. This process drives informed decision-making and predictive maintenance strategies.
Edge Computing Benefits:
Edge computing capabilities enable real-time data processing and analysis at the network’s edge. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage. By offloading computational tasks from the cloud to edge devices, organizations can enhance responsiveness and agility in IoT applications.
The Role of Vakoms in IoT Development
As a top-notch firm in software making, Vakoms focuses on creating custom IoT answers for specific client requirements. They are skilled in designing hardware, developing firmware, and integrating with the cloud. Vakoms provides comprehensive IoT services, helping businesses change and speed up their digital growth.
Custom IoT Solutions:
Vakoms collaborates directly with clients to design and develop customized Internet of Things (IoT) solutions. These solutions align with the clients’ strategic goals and specific industry needs. From initial conception to final deployment, Vakoms utilizes advanced technologies to deliver scalable and secure IoT ecosystems.
IoT Consulting:
Vakoms is providing comprehensive consulting services related to IoT development and implementation. They assist organizations in navigating the complexities of this process. They conduct feasibility studies, assess architecture, and evaluate technologies. This empowers clients to make informed decisions and maximize return on investment.
Continuous Support:
Vakoms offer continuous help and upkeep services. This guarantees IoT deployments work without issues as time passes. Vakoms handles any hardware problems and improves the efficiency of software. They supports their clients at every step, helping them fully leverage IoT solutions.
In Summary
IoT development represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with technology. It offers unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency gains. By understanding IoT’s key components, challenges, and best practices, beginners can embark on creating impactful IoT solutions. These solutions shape the future of connected ecosystems.